It’s important not to overlook the significance of sleep and mental health. Sleep plays a vital role in your overall well-being by aiding proper brain function, enhancing learning, decision-making, emotional control, and the ability to cope with change. Consistent lack of sleep can result in fatigue, irritability, and an increased risk of common mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. Up to one-third of the population may suffer from insomnia, which negatively affects mood, energy, relationships, and daily functioning.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for healthy sleep habits, as many have experienced “Coronasomnia” or increased sleep disturbances due to pandemic-related stress.
Impact of Sleep on Mental Health
There is a reciprocal relationship between sleep and mental health, where poor sleep can exacerbate mental health issues, and mental health problems can lead to sleep disturbances. Lack of sleep, particularly REM sleep, can negatively affect the brain’s ability to process emotional information and consolidate positive emotional content, influencing mood and emotional reactivity.
Sleep Deficiency and Mental Health Risks
Sleep deficiency can cause daytime fatigue, learning difficulties, focus and reaction problems, decision-making and problem-solving issues, lack of emotional control, and difficulty coping with change. It is linked to an increased risk of depression, anxiety, suicidal ideation, and risk-taking behavior.
In children, sleep deficiency may lead to hyperactivity, inattention, behavioral problems, mood swings, impulsivity, lack of motivation, and poor academic performance.
Sleep and Brain Function
Good sleep supports healthy brain function, learning, memory, and cognitive skills such as problem-solving and creativity. Lack of sleep can alter activity in parts of the brain responsible for decision-making, emotional control, and coping mechanisms.
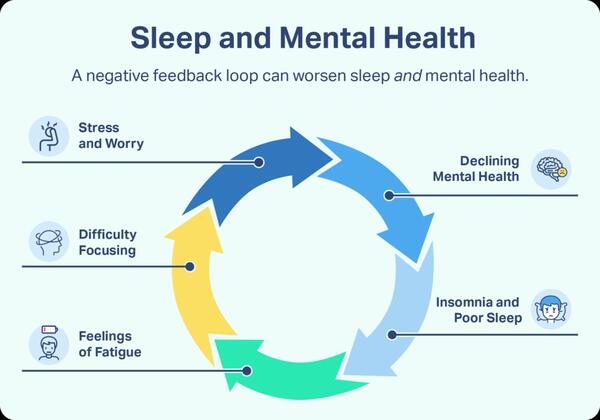
Mental Health Conditions and Sleep
Sleep Disturbances Across Mental Health Conditions
The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a significant increase in sleep problems, which are commonly referred to as ‘Coronasomnia‘. The increased stress causes this, as changes in daily routines, and reduced physical activity have resulted from the pandemic. Common sleep issues include difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early (insomnia), as well as problems that disrupt sleep like panic attacks, nightmares, or psychosis. Some people may also sleep excessively.
Various mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, trauma, paranoia, and mania can all have negative impacts on sleep in different ways. For example, anxiety disorders can cause restless nights, difficulty falling asleep, and frequent awakenings due to excessive worry and rumination.
Depression is often accompanied by insomnia or hypersomnia (excessive sleeping).
Trauma survivors may experience nightmares and sleep disturbances related to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Sleep Disorders and Mental Health
Sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea, are more common in people with psychiatric conditions and can worsen mental distress. Mental health conditions like depression, seasonal affective disorder, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, ADHD, and autism spectrum disorder all have strong links to sleep problems.
Sleep Hygiene and Lifestyle Factors
Sleep Hygiene Practices
To improve both sleep quality and mental well-being, cultivating healthy sleep habits through good sleep hygiene practices can be beneficial. Effective sleep hygiene strategies include:
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day, even on weekends.
- Creating a relaxing bedtime routine and a comfortable sleep environment that is cool, dark, and cozy.
- Limiting exposure to blue light from digital screens at least an hour before bedtime.
- Avoiding consumption of caffeine, alcohol, or large meals close to bedtime.
- Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation.
- Exercising regularly, but avoiding intense workouts close to bedtime.

Lifestyle Factors
Several lifestyle factors can influence sleep quality and contribute to sleep disturbances. Addressing these factors can help improve sleep and, consequently, mental well-being:
- Diet: Low-fiber, high-saturated fat, and high-sugar diets have been associated with poorer sleep quality.
- Exercise: Increasing exposure to bright light in the morning and afternoon can help regulate sleep-wake cycles.
- Screen Time: Avoiding screen time at least 1 hour before bed and making the bedroom a sleep-friendly environment can improve sleep quality.
Improving Sleep for Better Mental Health
Sleep Duration
The optimal amount of sleep for adults is between 7 and 8 hours per night. However, it’s worth noting that adults may need between 7 and 9 hours of restful sleep per night, depending on their age and individual circumstances. It’s essential to get enough high-quality sleep at the appropriate times to ensure overall health and well-being.

Impact of Poor Sleep
It is important to get enough sleep as lack of sleep can have negative physical and mental effects. These effects include increased risk for chronic health conditions and impaired cognitive abilities which can be comparable to being legally drunk. According to research, nearly 30% of adults have trouble falling or staying asleep, and more than 1 in 4 experience daytime sleepiness.
Strategies for Better Sleep
Improving and maintaining good sleep is crucial for maintaining good mental health. Some recommendations that could help are:
1. Highlighting the importance of sleep in public health campaigns.
2. Providing training and tools for healthcare professionals to recognize and manage sleep problems.
3. Ensuring access to cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia through programs like IAPT.
Improving sleep can play a vital role in managing mental health.
Conclusion
Sleep is an essential component of our overall well-being, and it has a significant impact on our mental health. The relationship between sleep and mental health is bidirectional, which emphasizes the importance of prioritizing healthy sleep habits. By practicing good sleep hygiene, engaging in regular exercise, and making necessary lifestyle changes, we can improve our sleep quality and reduce the risk of mental health issues.
If you suffer from chronic sleep difficulties, seeking professional help from sleep specialists or cognitive behavioral therapy can provide invaluable guidance. It is crucial to recognize the connection between sleep and mental health to foster a happier, healthier life. Prioritizing sleep can help us nurture our mental well-being and unlock our full potential for personal growth and fulfillment.
FAQs
1. What is important for maintaining good mental health and happiness?
Maintaining strong social connections is crucial for good mental health and overall happiness. Humans inherently seek connections and support and value interactions with others. Research shows that strong social relationships can contribute to better mental health and even extend life expectancy.
2. Why is sleep important for feeling happy?
Adequate sleep is essential because insufficient sleep leads to tiredness, difficulty concentrating and remembering, irritability, impaired judgment, and reduced physical coordination. All these factors negatively affect your mood, cognitive functions, work performance, learning abilities, and social interactions.
3. How do sleeping habits affect mental health and well-being?
Sleep plays a critical role in both mental and physical health by helping to repair and restore the brain and body. It allows for information processing, memory consolidation, and various maintenance processes that are vital for optimal daily functioning.
4. What is the key to achieving lifelong happiness?
According to Dr. Waldinger, maintaining healthy relationships is the key to lifelong happiness. Strong social ties not only contribute to emotional well-being but are also linked to lower rates of various chronic conditions such as diabetes, arthritis, and cognitive decline.
Also, you may like to read, Spiritual Practices for Deep Sleep: Cultivating Inner Peace for Restorative Rest.
