Many people snore, but how serious it is and what it means for your health can be different for everyone. Sometimes, snoring can be light, occasional, and unconcerned but other times it can mean there’s a bigger problem with how you breathe when you sleep.
If you and your partner snore often or sometimes, you might be thinking about stopping it. A lot of grown-ups snore regularly, among adults aged 30 to 60, about 44% of men and 28% of women snore regularly. Individuals over 60 years old likely snore regularly.
More on Snoring…
Snoring is the sound that occurs when air moves through your blocked airway, causing tissues at the top to touch and vibrate, making noise. Almost all adults snore from time to time.
For most people, snoring is little more than an embarrassment or annoyance. For others, however, snoring can cause problems or indicate an underlying health issue. Different people snore for different reasons. Trying a variety of tips can help you learn how to stop snoring while sleeping and determine if you need to talk to a doctor about your snoring.

For many people, snoring is just a minor inconvenience, maybe a bit embarrassing. However, for some people, it can signal bigger problems or health issues. Individuals snore for various reasons, so trying out different tips might help you stop snoring and figure out if you should speak with a doctor about it.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
According to experts, weight loss is one of the first and most crucial steps to treatments to try for snoring. Needless to say, this advice is specifically relevant for individuals who are overweight or obese.

Individuals with obesity are at a higher risk of snoring and developing obstructive sleep apnea. According to studies, losing body weight among those with a high body mass index can lessen both snoring and symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea. By adopting a healthy diet and incorporating regular exercise into your routine, you can shed those extra pounds and experience improvements in both snoring and overall health.
Try Throat Exercises
Throat exercises strengthen the muscles in the throat and palate and can help reduce snoring by preventing them from collapsing during sleep. Adding throat exercises into your daily routine, like singing, playing wind instruments, or practicing specific tongue and throat exercises which are recommended by speech therapists or sleep specialists. Consistent practice can lead to improvements in snoring over time.
Avoid Alcohol
Consumption of Alcohol not only worsens snoring but can also trigger obstructive sleep apnea in individuals who don’t typically have the condition. If you drink alcohol regularly, consider reducing your intake as the impact of alcohol on snoring and sleep depends on the amount consumed.

If snoring persists, try avoiding alcohol a few hours before bedtime or eliminating it from your routine altogether. Opt for herbal teas or relaxation techniques instead to promote restful sleep without the risk of exacerbating snoring.
Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can contribute to snoring by causing the throat and nasal tissues to become dry and sticky, leading to increased friction and obstruction of airflow. Make sure to stay hydrated throughout the day by drinking plenty of water. Limit your intake of dehydrating beverages such as caffeinated or alcoholic drinks, especially in the evening.
Laser-Assisted Uvulopalatoplasty
Laser-assisted uvulopalatoplasty is a surgical procedure used to address snoring and obstructive sleep apnea by resolving physical issues in the throat. In this surgery, the surgeon uses a laser to remove tissue from the uvula and soft palate, allowing for improved airflow in the throat and stiffening of the soft palate as tissue regrows in the treated areas.
However, though the surgery has been utilized for almost three decades, it has become controversial due to a significant occurrence of adverse side effects in recent years. Consequently, many surgeons have discontinued offering laser-assisted uvulopalatoplasty as a treatment option.

Avoid Smoking
Smoking cigarettes also contributes to increments in snoring. On the other side, quitting smoking can alleviate your snoring problem. Similarly, children with smoking parents tend to snore more. However, snoring is just one of the many health problems caused by smoking. Cigarettes contribute to around one-third of deaths from coronary heart disease and 90% of lung cancer cases in the U.S. They also shorten the lifespan of the average smoker by about 10 years.
Change Your Sleep Position
Sleeping in a bad posture or improper sleeping position can also cause snoring. Individuals are more likely to snore when they sleeping on their back (the supine position) compared to sleeping on their side (the lateral position).
Interestingly, the angle of your head might have a bigger impact on snoring than your overall body position, with snoring decreasing when the head is turned to the side.
If you notice that you are snoring and tend to sleep on your back, try shifting to your side when falling asleep. If changing your sleeping position is challenging, use pillows strategically to support your body, and keeping your head in a side position may help.
Use a Nasal Strip or Dilator
Internal and external nasal dilators aim to enhance airflow during sleep, potentially reducing snoring. Both types of nasal dilators are typically small, flexible strips designed to open the nasal passages using tension.
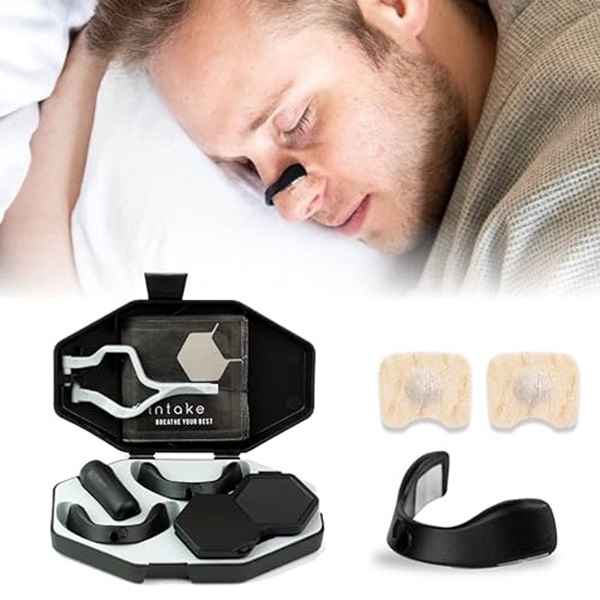

External nasal dilators, also known as nasal strips, are adhesive strips applied to the outside of the nose. They pull outward, lifting the skin and opening the nasal passages. Likewise, internal nasal dilators work similarly but from the inside, pushing outward. Research indicates that both types can reduce snoring, although internal dilators are more likely effective.
Try Anti-Snoring Mouthpiece
There are several dental devices to alleviate snoring. These anti-snoring mouthpieces are larger and sit in the mouth all night so it can take more getting used to than nasal strips. These devices, known as anti-snoring mouthpieces, resemble mouthguards and are available over the counter. They typically come in two varieties,
Mandibular advancement devices (MADs): They function by keeping the lower jaw in a forward position. Numerous MADs are adjustable, allowing users to customize for comfort and effectiveness.
Tongue retaining devices (TRDs): Tongue retaining devices are mouthpieces designed to secure the tongue in position, preventing it from slipping backward towards the throat.
These anti-snoring dental devices not only reduce snoring but also potentially improve mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea. However, it’s important not to self-diagnose or self-treat sleep apnea. If considering a dental device for sleep apnea, it’s crucial to consult your doctor for approval and guidance.
When to see a doctor?
If snoring persists despite trying various self-help strategies, it may be a sign of an underlying sleep disorder such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). OSA is a serious condition characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep, often accompanied by loud snoring.
If you suspect you may have OSA or if your snoring is causing significant disruption to your life, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment options.
Frequently Asked Question
What causes snoring?
Snoring occurs when the flow of air through the mouth and nose is obstructed during sleep, leading to vibrations in the throat tissues. Common causes include obesity, sleep position, alcohol consumption, and nasal congestion.
Can losing weight help reduce snoring?
Yes, for many people, losing weight can significantly reduce or eliminate snoring. Excess weight, especially around the neck area, can put pressure on the airway, increasing the likelihood of obstruction and snoring.
You may also like to read, What is Somniphobia? Learn about its Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
