The Impact of Sleep Patterns on Blood Sugar Regulation: Exploring the Connection
Introduction to Sleep Patterns and Blood Sugar Regulation
Exploring the intricacies of health can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to understanding blood sugar regulation and sleep patterns. These two aspects of well-being are more connected than we initially thought, and they both play a vital role in maintaining overall health. Sleep is an essential function that provides the body with the downtime it needs to repair, regroup, and prepare for the challenges of a new day. Blood sugar regulation ensures that the body has the right amount of energy at the right times, preventing both short-term fluctuations and long-term health issues. Understanding the interaction between these two aspects of health can lead to new ways of achieving a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Quality and quantity are both crucial when considering the importance of sleep. Different sleep stages contribute differently to bodily functions, including hormone regulation that affects blood sugar levels. Blood sugar regulation isn’t just about diet; it’s also influenced by how well the body can process and use glucose, which sleep patterns can significantly affect.
In this exploration of how sleep patterns impact blood sugar regulation, we’ll delve into the mechanisms that connect these two critical aspects of health, with scientific research and expert insights backing up the discussion. By understanding the relationship between these two aspects of health, you can make informed decisions to improve your well-being, paving the way for a healthier life.
Understanding Blood Sugar Regulation
Blood sugar regulation is a complex process that involves multiple organs and hormones working together to ensure that your body has sufficient energy to function properly. The process also ensures that blood sugar levels remain stable and don’t become too high or too low. The pancreas plays a crucial role in this process by producing insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream. Another hormone, glucagon, works against insulin by raising blood sugar levels when they become too low.
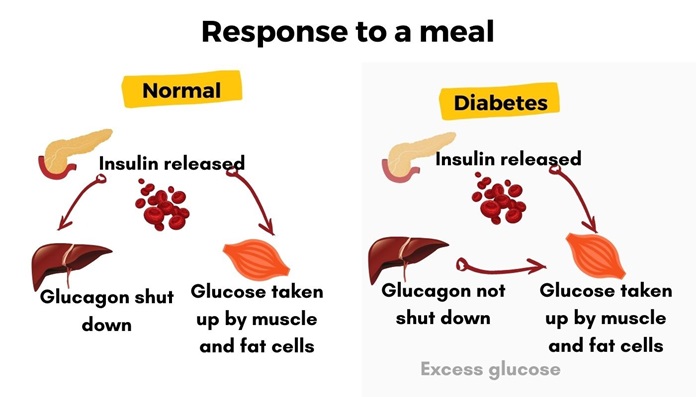
Maintaining a delicate balance between insulin and glucagon is crucial for maintaining homeostasis and a stable internal environment. However, various factors, including diet, physical activity, stress, and sleep, can disrupt this balance. Changes in any of these areas can lead to imbalances in blood sugar levels, which can cause conditions like insulin resistance, prediabetes, or diabetes.
The body’s ability to regulate blood sugar is not only critical for preventing chronic conditions but also essential for daily functioning. Glucose is the primary energy source for your cells, and without proper regulation, you may experience energy spikes and crashes throughout the day, which can affect your mood, concentration, and overall health.
The Role of Sleep in Regulating Blood Sugar Levels
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining good health by affecting various physiological processes, including the regulation of blood sugar. When we sleep, our body undergoes several changes that impact how it processes and utilizes glucose. For instance, sleep has an impact on the body’s sensitivity to insulin, and poor sleep can result in reduced sensitivity. This means that the body needs more insulin to process glucose, which puts extra pressure on the pancreas and may increase blood sugar levels.
Moreover, sleep influences the hormones that regulate appetite, such as ghrelin and leptin. Ghrelin stimulates appetite, while leptin signals satiety. When sleep patterns are poor, these hormones may become imbalanced, leading to an increase in hunger and a preference for high-carbohydrate, high-sugar foods, further complicating blood sugar regulation.
The relationship between sleep and blood sugar regulation is bidirectional. Just as poor sleep can result in imbalances in blood sugar levels, high blood sugar levels can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to a vicious cycle that can be challenging to break. This connection emphasizes the importance of addressing both sleep and blood sugar regulation to achieve optimal health.
Research on the Impact of Sleep Patterns on Blood Sugar Regulation
The scientific community has been increasingly interested in the connection between sleep patterns and blood sugar regulation in recent years. Many studies have highlighted this relationship, indicating that people who experience poor sleep quality or insufficient sleep duration have a higher risk of developing blood sugar regulation issues, including type 2 diabetes.
One groundbreaking study has found that even a single night of partial sleep deprivation can decrease insulin sensitivity, demonstrating the immediate impact of sleep on blood sugar levels. Additionally, research has focused on the effects of sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, on blood sugar regulation, finding significant correlations between obstructive sleep apnea and the risk of developing diabetes.
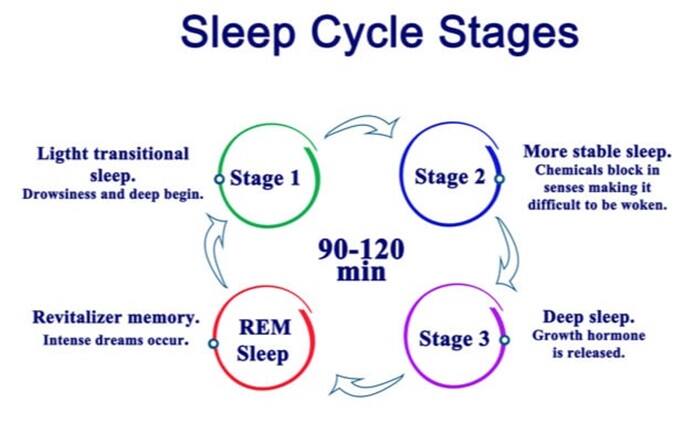
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels During Sleep
The interplay between sleep and blood sugar regulation is intricate, and there exist several factors that can affect blood sugar levels during sleep. Notably, the timing and composition of the last meal before bedtime can influence how the body manages blood sugar levels throughout the night. Consuming a large, high-carbohydrate meal near bedtime can disrupt the body’s natural hormonal processes, leading to increased blood sugar levels during sleep.
Another critical factor that impacts blood sugar levels during sleep is physical activity. Regular exercise can enhance insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to regulate blood sugar levels during both waking and sleeping hours. However, the timing of exercise can also influence blood sugar levels during sleep, with late-night exercise potentially leading to fluctuations.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Blood Sugar Regulation
Sleep deprivation can have a profound impact on the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. When a person is sleep-deprived, their insulin sensitivity decreases, making it harder for the body to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. This can lead to higher fasting glucose levels and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, sleep deprivation alters the hormones that control hunger and satiety, leading to an increased appetite and a preference for high-sugar and high-fat foods, further exacerbating issues with blood sugar regulation.
The impact of sleep deprivation extends far beyond just blood sugar regulation. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to a range of health problems, including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and obesity. All of these conditions are closely linked to blood sugar regulation. It is, therefore, vital to address sleep issues as part of a comprehensive approach to overall health and well-being.
Tips for Improving Sleep Patterns and Blood Sugar Control
To improve sleep patterns and blood sugar control, establish a consistent sleep schedule that aligns with your body’s internal clock. Create a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation and reduces stress and anxiety. This may include reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing meditation.

It is crucial to regulate your sleep and blood sugar levels by maintaining a balanced diet. You must focus on consuming whole foods that are rich in fiber, healthy fats, and proteins. Ensure that you avoid consuming large meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime, as these can adversely affect your sleep quality and blood sugar regulation.
Regular physical activity is essential to improve your sleep patterns and blood sugar control. Exercise can help improve your body’s insulin sensitivity, making it easier to regulate blood sugar levels. However, it’s important to find the right time for exercise, as working out too close to bedtime can interfere with your sleep quality. By making these lifestyle changes, you can improve your overall health and well-being.
Conclusion: Importance of Healthy Sleep Patterns for Blood Sugar Regulation
The correlation between sleep patterns and blood sugar levels is a well-established fact that should not be ignored. These two factors have a significant impact on each other, which can influence the overall health and well-being of an individual in profound ways. Therefore, it is essential to understand the connection between them, as it can be crucial for anyone seeking to improve their health.
By addressing both sleep patterns and blood sugar regulation simultaneously, individuals can make significant strides toward achieving a balanced and healthy lifestyle. Making some simple but effective changes to improve sleep patterns and regulate blood sugar levels can lead to visible improvements in overall health, energy levels, and mood. It is a journey worth embarking on because it has the potential to transform one’s life in significant ways.
FAQ
1. How do sleep patterns affect blood sugar regulation?
Sleep patterns have a significant impact on regulating the levels of glucose in the blood. When a person experiences poor quality sleep or not enough sleep, it can disrupt the body’s ability to regulate glucose properly. This disruption may lead to higher blood sugar levels and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
2. What happens to blood sugar levels during sleep?
Getting proper sleep is crucial for regulating the glucose levels in our blood. If we don’t get enough quality sleep, it can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate glucose effectively, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
3. Can improving sleep patterns help regulate blood sugar levels?
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, practicing good sleep hygiene, and addressing any underlying sleep disorders can help promote better sleep quality and improve overall metabolic health, which positively impacts blood sugar regulation.
Also, read more about, Couch Comfort vs. Health: Unveiling the Health Considerations of Sleeping on Sofas.